📝 Challenge Overview
You boot an instance and land on a web login page. Inspecting the page source reveals a commented-out string that looks like a simple substitution cipher (ROT13 / Caesar). Decoding it reveals an instruction to add a special HTTP header (X-Dev-Access: yes) to bypass the login. By intercepting the login request (e.g., with Burp Suite) and adding that header, the server accepts the request and returns the flag. This challenge demonstrates the value of checking page source and comments, and of using simple decoding tools and an intercepting proxy.
🔎 Step 1: Open the web page and inspect source
- Start the instance and open the provided URL in your browser.
- Right-click → View Page Source (or open Developer Tools → Elements).
- You find this commented line in the HTML:
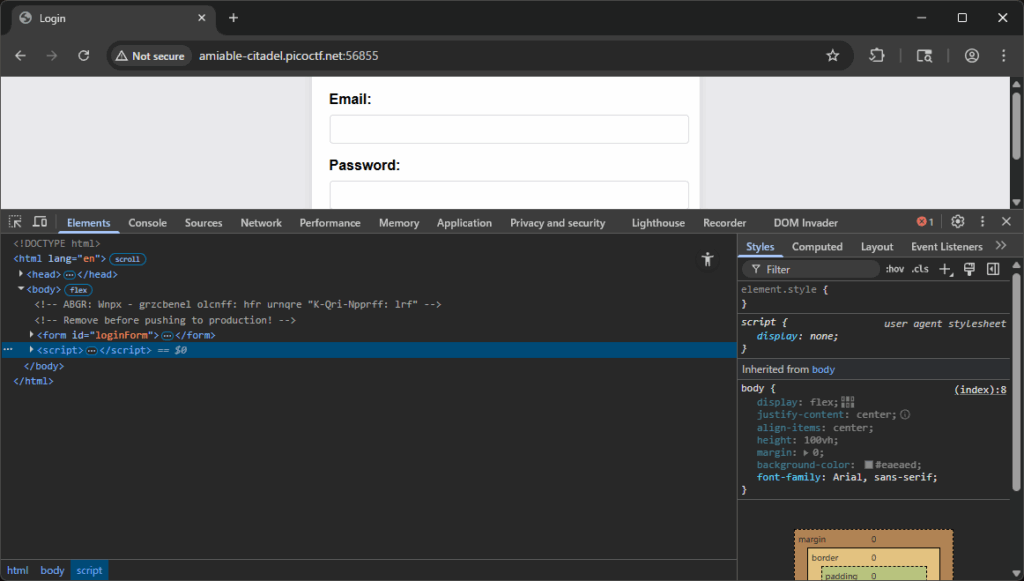
<!-- ABGR: Wnpx - grzcbenel olcnff: hfr urnqre "K-Qri-Npprff: lrf" -->
📝 Explanation: Comments and developer notes are visible in page source and sometimes contain hints or debugging information. Never skip reading comments when solving web CTFs.
🔐 Step 2: Recognize and decode the cipher (ROT13)
- The comment contains only letters (no digits), which suggests a Caesar-style substitution like ROT13.
- Decode with a quick Python snippet:
import codecs cipher = '<!-- ABGR: Wnpx - grzcbenel olcnff: hfr urnqre "K-Qri-Npprff: lrf" -->' decoded = codecs.decode(cipher, 'rot_13') print(decoded)
- Running it prints:
<!-- NOTE: Jack - temporary bypass: use header "X-Dev-Access: yes" -->
📝 Explanation: ROT13 rotates each letter by 13 positions. It’s commonly used in CTFs to obfuscate short hints. Decoding reveals the header name and value to use.
🔁 Step 3: Intercept the login request and add the header
- Configure your browser to use Burp Suite (or another intercepting proxy).
- In Burp Proxy, enable Intercept and submit the login form in the browser. Burp will capture the POST/GET request.
- In the request editor (Repeater or Proxy → Intercept), add the header:
X-Dev-Access: yes
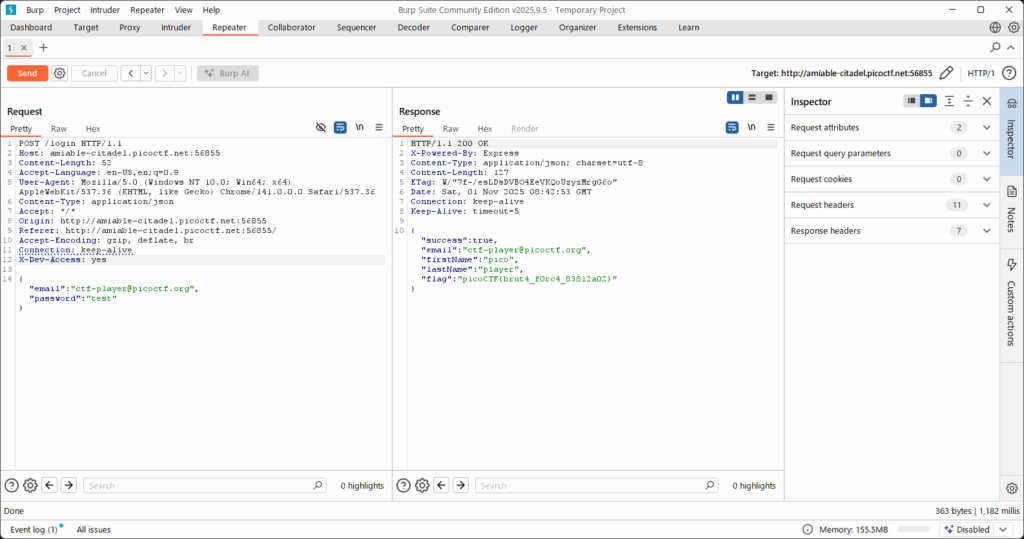
- Forward / send the modified request to the server. Inspect the response.
📝 Explanation: Adding the header simulates the developer bypass hinted in the comment. Intercepting proxies let you modify requests on the fly (headers, body, cookies) to test server behavior.
🏁 Capture the Flag
🎉 After sending the request with the added header, the server responds with the flag:picoCTF{brut4_f0rc4_83812a02}
📊 Summary
| Step | Command / Action | Purpose | Key Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Open page → View Page Source | Find hidden comments or hints | Found commented ROT13 string |
| 2 | python3 ROT13 decode snippet | Decode the obfuscated hint | Revealed X-Dev-Access: yes |
| 3 | Intercept request in Burp → add header X-Dev-Access: yes | Simulate developer bypass at the server | Server returns flag picoCTF{...} |
💡 Beginner Tips
- 🔎 Always check page source, not just rendered pages—comments often contain useful hints.
- 🧩 If a scrambled-looking alphabetic string appears, try ROT13 or simple Caesar shifts first. Quick decoders: Python
codecs.decode(...,'rot_13'), CyberChef, or online ROT13 tools. - 🛠 Use an intercepting proxy (Burp, OWASP ZAP) to safely modify requests — add headers, change bodies, replay requests.
- ⚠️ Only test such techniques on authorized targets (CTFs or systems you own). Don’t tamper with third-party sites without permission.
🎓 What you learn (takeaways)
- Comments in HTML can leak developer-only bypasses or sensitive hints.
- ROT13 is a fast, common obfuscation — learn to spot and decode it instantly.
- HTTP headers can control server logic; altering them may change behavior if the server trusts client-supplied headers without validation.
- Intercepting proxies are essential tools for web testing and exploitation in CTFs.
⚡ Short explanations for commands / techniques used
- 🧾 View Page Source / Inspect Element
- What: Shows raw HTML including comments.
- Why: Hidden hints often placed in comments are only visible here.
- 🔁 ROT13 decoding (
codecs.decode(...,'rot_13'))- What: Simple substitution cipher rotating letters by 13.
- Why: Quickly decodes obfuscated developer notes.
- 🕵️ Burp Suite (Proxy / Repeater / Intercept)
- What: Intercepting proxy to capture and modify HTTP(S) traffic.
- Why: Lets you add/modify request headers (like
X-Dev-Access) to test server responses. - How: Intercept the login request → edit request headers → forward or send → inspect response.
- 🧪 Add custom header
X-Dev-Access: yes- What: Insert a new HTTP header in the outgoing request.
- Why: The server was coded to accept this header as a temporary bypass (per the decoded comment).
Leave a Reply