Description
A digital ghost has breached my defenses, and my sensitive data has been stolen! 😱💻 Your mission is to uncover how this phantom intruder infiltrated my system and retrieve the hidden flag.To solve this challenge, you’ll need to analyze the provided PCAP file and track down the attack method. The attacker has cleverly concealed his moves in well timely manner. Dive into the network traffic, apply the right filters and show off your forensic prowess and unmask the digital intruder!Find the PCAP file here Network Traffic PCAP file and try to get the flag.
🧩 Challenge Description
You are given a file with the .pcap extension.
A PCAP (Packet Capture) file contains recorded network traffic — basically, it’s a log of what happened over a network connection.
Our goal: open this PCAP file, analyze it, and find the hidden flag.
🧰 Step 1: Opening the PCAP file in Wireshark
The easiest way to analyze .pcap files is to use Wireshark, a free and powerful GUI tool for viewing network packets.
👉 Wireshark lets you see every packet (piece of network data), including source, destination, time, and contents.
Open the downloaded file in Wireshark and scroll through the packets.
You’ll notice some strange text that looks like Base64-encoded strings — they often end with = or ==.
🔠 Step 2: Recognizing Base64 Encoded Data
Base64 is a common way to encode binary data as text.
If you see random-looking letters ending in = or ==, that’s a strong hint that it’s Base64.
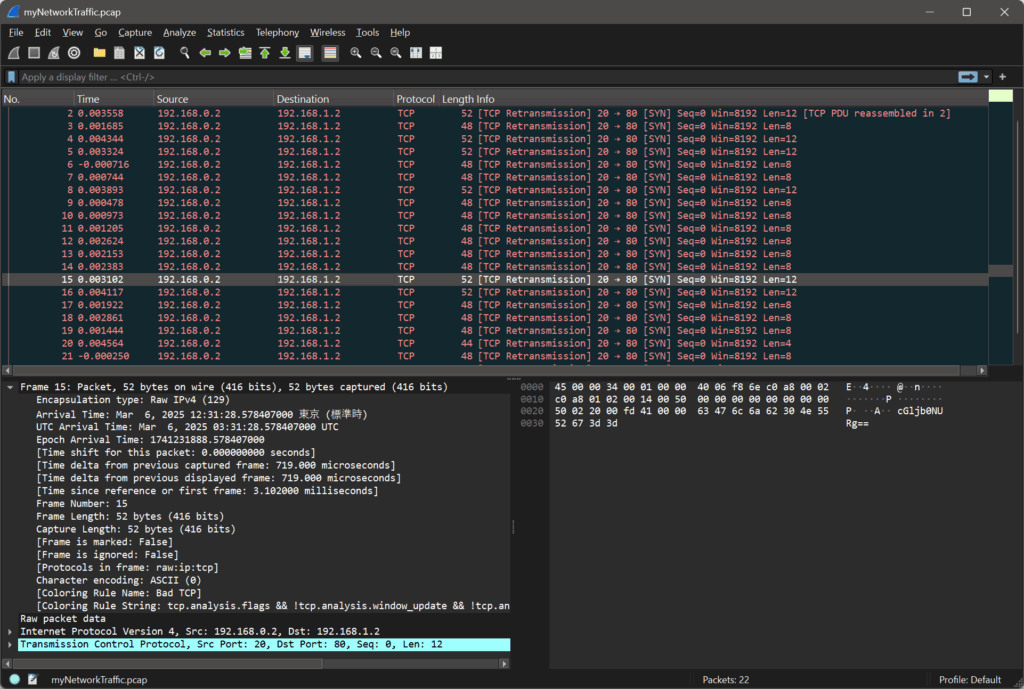
There is a lot of information, so look at length other than 48 bytes.
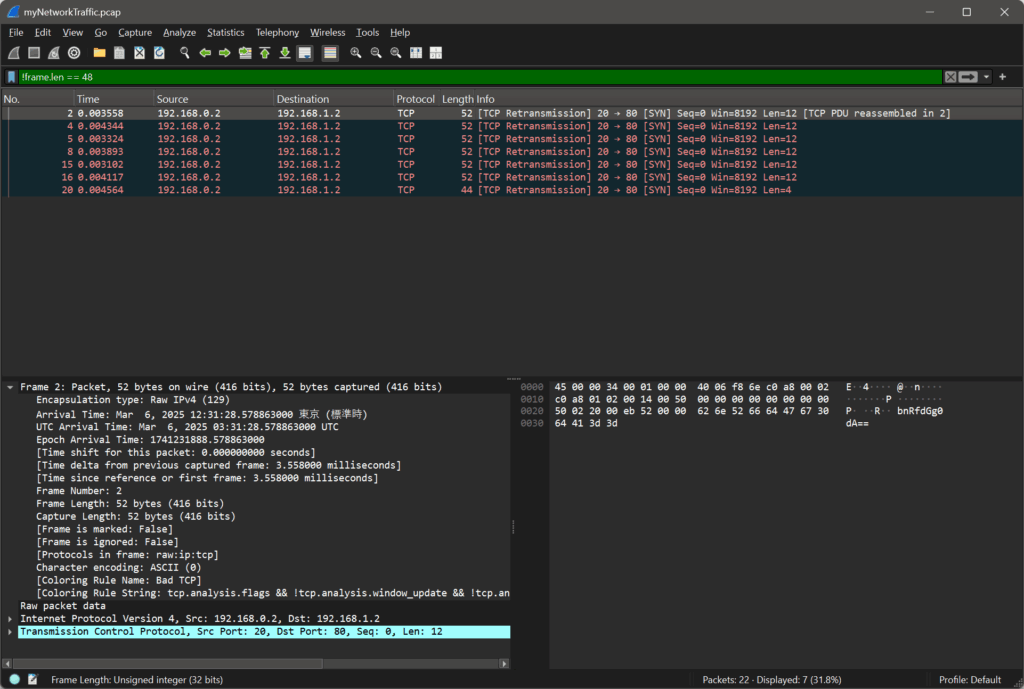
Here’s what some of the captured data looks like:
31.28.5788 bnRfdGg0dA== 31.28.5796 NjZkMGJmYg== 31.28.5786 ezF0X3c0cw== 31.28.5791 XzM0c3lfdA== 31.28.5784 cGljb0NURg== 31.28.5794 YmhfNHJfOQ== 31.28.5798 fQ==
Each line shows:
- A timestamp (the time the packet was captured)
- A Base64 string (the data payload)
⏱ Step 3: Sorting the packets by time
The data seems out of order, so let’s sort it chronologically by the timestamp:
31.28.5784 cGljb0NURg== 31.28.5786 ezF0X3c0cw== 31.28.5788 bnRfdGg0dA== 31.28.5791 XzM0c3lfdA== 31.28.5794 YmhfNHJfOQ== 31.28.5796 NjZkMGJmYg== 31.28.5798 fQ==
Once we have them ordered correctly, we can decode each Base64 string.
🐍 Step 4: Decoding Base64 in Python
Let’s write a short Python script to decode all these Base64 strings and combine them.
import base64
cipher = [
"cGljb0NURg==",
"ezF0X3c0cw==",
"bnRfdGg0dA==",
"XzM0c3lfdA==",
"YmhfNHJfOQ==",
"NjZkMGJmYg==",
"fQ=="
]
plain = ""
for c in cipher:
decoded = base64.b64decode(c).decode()
plain += decoded
print(plain)
✅ Explanation:
import base64→ loads the Python library for Base64 encoding/decodingb64decode()→ converts Base64 text back into readable ASCII text- The loop joins all decoded parts together into one final string
▶️ Step 5: Running the Script
Run the script in your terminal:
$ python3 decode.py
Output:
picoCTF{1t_w4snt_th4t_34sy_tbh_4r_966d0bfb}
🎉 We’ve found the flag!
🏁 Final Flag
picoCTF{1t_w4snt_th4t_34sy_tbh_4r_966d0bfb}
🧠 Summary
| Step | Tool / Command | Purpose | Key Finding |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Wireshark | View PCAP file contents | Found encoded packets |
| 2 | Base64 | Recognize encoded data | Strings ending in = |
| 3 | Sorting | Order packets by time | Built proper sequence |
| 4 | Python + base64 | Decode data | Revealed flag text |
💡 Beginner Tips
.pcapfiles are network captures, often containing hidden messages in packet data.- Wireshark is your best tool for visually exploring them.
- If you see strange letter strings with
=, think Base64! - Python’s
base64module is perfect for quick decoding.